As a marketer, you know that search engine optimization, aka SEO, is a key long term focus for your business. Page one rankings on Google and a steady flow of organic traffic is the goal of any business marketer who knows their stuff. But then, along comes a negative SEO attack.
Hold up! What is a negative SEO attack?
What even is the point in a negative SEO attack? And, more importantly, how can you make sure it never happens to you.
There is a lot to take in, but in this post we’re going to answer all those questions and help you avoid falling victim to the impact of negative SEO.
What is negative SEO?
As you might expect, negative SEO is any strategy or campaign that causes a website to lose search engine rankings.
However, negative SEO attacks are often an automated process that generates spammy links. They are often carried out by shady business competitors or someone who specifically wants your search rankings to be compromised.
Negative SEO can also be generated by poor quality link building on the part of the website owner – so it isn’t always an external factor that is to blame!
How to spot negative SEO
The most obvious result of negative SEO attacks is that you lose rankings, or you find yourself ranking for unusual or irrelevant keywords.
As a digital marketer, you use a number of keyword research tools (of course), and you obviously monitor your rankings on a regular basis. One or all of these factors may indicate that you’ve been impacted by negative SEO:
- A large loss or decrease in keyword rankings, especially for your top ranking search terms
- Unusual anchor text, often spammy or unrelated to your industry
- Lots of new backlinks from what appear to be spam sources
- A sudden run of bad reviews, often similar in content and from people who most likely never have been your target audience
- New or unusual content posted on your site, this may be within existing content or new pages created (a form of SEO spam)
- Lots of content duplication – content scraping is one way to get penalized by Google
Not all of these will show up in your research tools, and some may not be visible at all.
But often one will be accompanied by another – for example if someone scrapes your content, they may link back to your site with a random anchor text.
What causes negative SEO?
The effects of negative SEO are normally a result of what Google considers to be bad practice for content creation. In marketing speak, it’s usually black hat SEO practices, whether that’s accidental or intentional.
Some common causes of negative SEO are:
1. Bad/spam backlinks
As a good digital marketer, you obviously focus on winning good quality backlinks from relevant sites. Spam backlinks often have the opposite effect, at least in the long run.
These low quality backlinks can also be a source of junk website traffic, and can lead to Google penalties, including loss of search visibility or rankings.
2. SEO spam attacks
This sneaky practice is a popular black hat SEO technique used by low grade digital marketers. By inserting irrelevant links into a website, content scraping or misrepresenting content on a site (known as cloaking) a sneaky marketer can get some quick wins for their clients.
You might find that content on your website is linking to irrelevant content including adult themes. Or, you may spot the really weird Japanese spam attack, where your site links to sites using Japanese characters.
Of course, this SEO spam damages your site, including your search rankings, and doesn’t even serve their clients well in the long run.
You can read more about SEO spam attacks on our blog.
3. Fake reviews
It’s easy to buy reviews in bulk from a number of places on the internet. How do fake negative reviews damage your SEO? Mostly, the issue is with brand reputation and the loss of traffic from reviews sites.
If you use extensions in your ads, you can also find that your star rating drops, which obviously doesn’t look good when compared to your competitors.
4. Removal of backlinks
If you’ve spent time curating quality dofollow links from a broad variety of websites, it can be pretty disheartening to see that ‘lost’ link in your search console.
But it can be quite simple for a competitor to put together a bulk email asking websites to either remove your link or make it nofollow. Why? Well, if you’re ranking well in the organic results and your competitor wants to leapfrog you, they could get an easy win if you lose a few of those quality links.
Another technique is to use the DMCA (digital millennium copyright act) to request a link removal. DMCA is supposed to protect intellectual property, for example a website hosting bootleg films or music. But, it can also be used as part of a coordinated negative SEO attack.
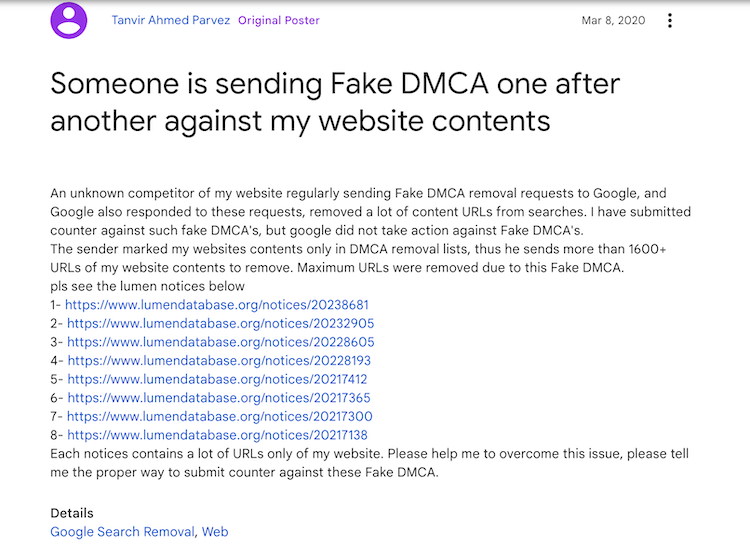
5. Content scraping
Sites with duplicate content can be penalized by Google. So, although it’s not guaranteed to knock you off the ranklings, content scraping can be damaging.
This is usually when the scraped content is repurposed to link to other websites, or used to
Often performed by automated processes, such as bots, content scraping can be one of the hidden forms of SEO spam attacks. The best way to block this form of activity is to block bot traffic on your website.
6. Spam comments and link farms
Some of the more damaging forms of black hat SEO are those where links are posted without real regard for the location. An obvious version of this is the spam comments with a URL inserted.
You’ve probably seen these if you run a site with a comment box – they usually look something like this:
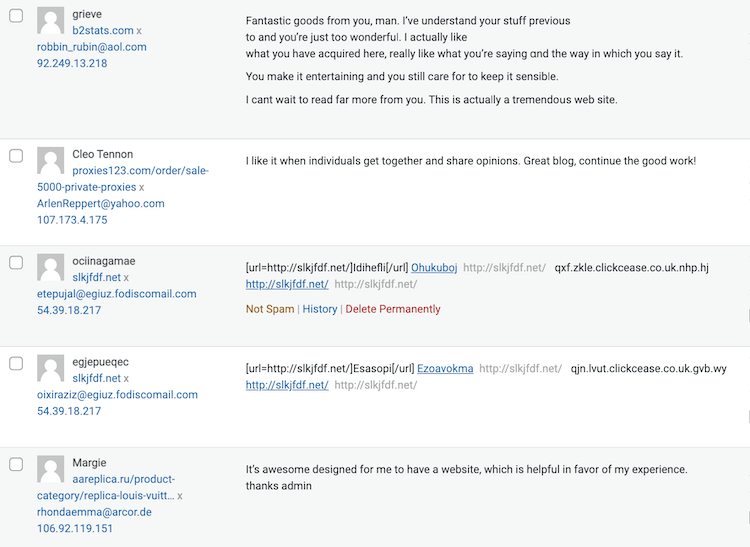
As you’ll notice, there are usually backlinks within the name/poster’s details, and often within the comment too.
Is this good SEO?
Actually, comment spam is seen as low quality links, and usually gets flagged up for a Google penalty. Those of you search engine veterans will remember that comments used to be a valid source of backlink – but this isn’t the case with contemporary search engine optimization.
Another one is links from PBNs, also known as Private Blog Networks, or link farms. Again, this is an outdated form of creating backlinks, and one seen as being spammy.
High volumes of comment spam or link farm spam can lead to a high spam score and points docked in the battle for search rankings. You probably already know to avoid these negative SEO tactics in your own optimization campaigns, so it can be quite damaging if someone else does it for you.
Read more about spam bots and how they affect your marketing
How can you avoid negative SEO?
The best way to ensure your website is optimized as well as can be is to focus on purely white hat SEO strategies. This means:
- Focus on relationship-building, as well as link building
- Make sure your site is fast and mobile optimized
- Have a content strategy and stick to it
- Use social media to spread your latest posts
- Create content for your customers, not for search engine crawlers (but also optimize where possible)
Of course, you already know that focusing on white hat SEO is the best approach. What about those factors that you can’t control? What about damaging practices for sneaky competitors or malicious botnets?
Set up link alerts

One good way to monitor new and lost links is to create a new links alert for your domain within your keyword research tool. Ahrefs, SEMRush and other tools such as SERPstat will allow you to set up an email alert each time you gain or lose a link.
It’s a good idea to set up a unique email address for this one, such as linkalerts@yourdomainname.com.
You can then check this every few days, or weekly, and if you notice any strange activity, you can take action (if action is needed).
The most common form of action to take is disavowing links that you have identified as spammy. But using link alerts and monitoring your backlink profile and the referring domains or anchor text can help you stay on top of any potential issues.
Disavow bad links
There are several schools of thought with the issue of bad links impacting your SEO efforts.
Some believe that too many spammy links can definitely lead to Google penalties. But since Google actually looks at bad links and devalues them, the other school of thought is that you don’t need to do anything to combat spam links.
Google even states this on their disavow help form:
“Google works very hard to make sure that actions on third-party sites do not negatively affect a website. In some circumstances, incoming links can affect Google’s opinion of a page or site. For example, you or an SEO that you’ve hired may have built bad links to your site via paid links or other link schemes that violate our quality guidelines. First and foremost, we recommend that you remove as many spammy or low-quality links from the web as possible.”
If you have seen some form of negative SEO attack, and you have a ton of spammy links pointing to your site, you might want to start disavowing.
The good news is that it’s relatively straightforward.
You’ll also fund a pretty useful guide to disavowing links with Google’s disavow tool.
But to simplify it here; you simply put together a list of the links you want to block (export to a CSV and upload to an Excel or Sheets spreadsheet), and then use the disavow tool to upload to Google.
Monitor fake reviews

When it comes to fake reviews, it can be hard to block them. But the best thing to do is to have a process of checking your reviews every few weeks, or monthly.
Of course, it’s good practice anyway, especially if it means you get to respond to problems or negative comments from your customers. But it can also help you spot if there has been a trend of bad reviews in a short time frame.
But what can you do if you are seeing a flood of bad reviews (or even a steady trickle)?
The obvious first thing to do is work out if there is an obvious reason for them. If there isn’t, and you’re sure the bad reviews are in fact fake reviews, you can try and report them to the review platform.
There are no guaranteed results here though, as it will depend on the policy of the reviews platform. But… If you don’t ask, you don’t get.
Another way to fight back against fake reviews?
Ask your happy customers to leave you good reviews. Run a campaign to get your average star rating back up and hopefully that can counteract the bad reviews.
Bot blocking
Not all aspects of negative SEO will incorporate bots, but many do…
Typical bot activity related to negative SEO attacks can include:
- SEO spam
- Content scraping
- Link injection
- Spam comments
- User agent spoofing
Using bot blocking software, such as Bot Zapping by ClickCease, will eliminate or greatly reduce the chances of most of these sneaky practices happening on your site.
Bot blocking also helps to avoid other forms of cyber attack, such as DDoS attacks, spam bots and account takeovers or brute force logins.
In the modern digital landscape, bot blocking is a necessary tool for any business, especially those running online shops, using PPC advertising or hosting an online database.
Find out more about bot traffic and how it affects your business
Is negative SEO a big problem?
The truth is that negative SEO is still a relatively niche form of cyber attack. The average business website is more likely to be hit by a DDoS attack, brute force logins or some form of spam attack.
But that’s not to say it can’t or won’t happen to you.
By putting some processes in place, such as keeping track of your reviews and incoming or lost links, you can be forewarned if some form of negative SEO attack does impact you.
And by blocking bot activity on your site, you can be assured that content scrapers and spam injection shouldn’t be an issue for you.
ClickCease offers marketers protection for both their paid ads on Google, Facebook and Bing (click fraud protection). And now, you can also protect direct and organic traffic on your WordPress site too with Bot Zapping.
